Different Types of Air Compressors
If you work in an industry that requires the use of air-powered tools, then you know how important it is to have the right air compressor. There are several different types of air compressors available, each with its own unique set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the differences between these types of air compressors can help you choose the right one for your needs.
Air compressors can be divided into two main categories: positive displacement compressors and dynamic compressors. Positive displacement compressors work by trapping air in a chamber and then reducing the volume of that chamber to compress air. Dynamic compressors, on the other hand, work by using high-speed impellers or rotors to accelerate air and then slowing it down to compress it. Each type of compressor has its own set of pros and cons, and the right choice will depend on your specific needs.
Key Takeaways
-
There are two main categories of air compressors: positive displacement and dynamic compressors.
-
Positive displacement compressors work by reducing the volume of a chamber to compress air, while dynamic compressors use high-speed impellers to accelerate and compress air.
-
Choosing the right air compressor will depend on your specific needs and the advantages and disadvantages of each type.
How do air compressors work?
Air compressors are devices that convert power into potential energy stored in pressurized air. They are used in a wide range of applications, including powering pneumatic tools, inflating tires, and providing compressed air for industrial processes.
Compressed air is created when air is compressed, which increases the air pressure and reduces its volume. This compressed air can be stored in a tank and used later when needed. The amount of compressed air that a compressor can produce is measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), and the pressure it can generate is measured in pounds per square inch (PSI).
There are two main types of air compressors: positive displacement and dynamic. Positive displacement compressors work by trapping air in a chamber and then reducing the volume of that chamber to compress the air. Dynamic compressors work by accelerating air and then slowing it down, which increases the air pressure.
Positive displacement compressors can be further divided into reciprocating, rotary screw, and rotary vane compressors. Reciprocating compressors use pistons to compress air, while rotary screw compressors use two interlocking screws to compress air. Rotary vane compressors use a rotor with vanes that slide in and out of slots to compress air.
Dynamic compressors can be further divided into centrifugal and axial compressors. Centrifugal compressors use a spinning impeller to accelerate air and then a diffuser to slow it down and increase the pressure. Axial compressors use a series of rotating and stationary blades to compress air.
When choosing an air compressor, it is important to consider the CFM and PSI requirements of the tools or processes that will be using the compressed air. It is also important to consider the size and portability of the compressor, as well as its noise level and maintenance requirements.
Overall, understanding the different types of air compressors and their applications can help you choose the right compressor for your needs and ensure that you have a reliable source of compressed air.
Positive Displacement Compressors

Positive displacement compressors are a type of air compressor that work by trapping air in a compression chamber and then reducing the volume of the chamber to increase the air pressure. This process is repeated over and over again to produce a continuous flow of compressed air. Positive displacement compressors are known for their high efficiency and reliability, making them a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
Reciprocating Compressors
Reciprocating compressors are a type of positive displacement compressor that use a piston to compress air. These compressors work by drawing air into a cylinder through an intake valve, then compressing the air with a piston that moves back and forth inside the cylinder. Reciprocating compressors are commonly used in applications that require high pressure and low flow rates, such as in industrial processes or for powering pneumatic tools.
Rotary Screw Compressors

Rotary screw compressors are another compressor type that use two rotating screws to compress air. These compressors work by drawing air into the space between the screws and the compressor housing, then compressing the air as the screws rotate and the volume of the space between them decreases. Rotary screw compressors are known for their high efficiency and ability to deliver a continuous flow of compressed air, making them a popular choice for applications that require a steady supply of compressed air.
Scroll Compressors
Scroll compressors are a type of positive displacement compressor that use two interlocking spiral scrolls to compress air. These compressors work by drawing air into the space between the scrolls and the compressor housing, then compressing the air as the scrolls rotate and the volume of the space between them decreases. Scroll compressors are known for their high efficiency and low noise levels, making them a popular choice for applications that require quiet operation, such as in medical or dental offices.
Here’s a video from Copeland Scroll with a great explanation on how scroll compressors work.
Vane Compressors
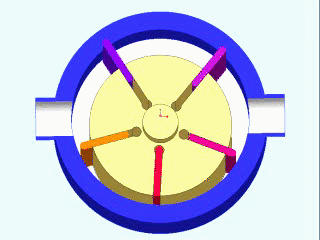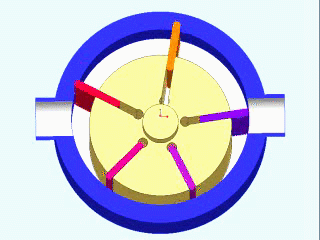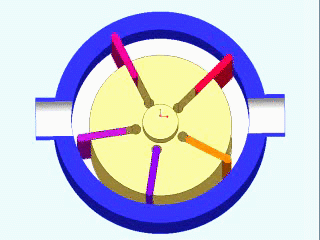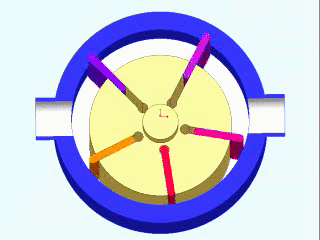
Vane compressors are a type of positive displacement compressor that use a series of sliding vanes to compress air. These compressors work by drawing air into a cylinder through an intake valve, then compressing the air with a rotor that has a series of slots that hold the vanes. As the rotor rotates, the vanes slide in and out of the slots, compressing the air as they do so. Vane compressors are known for their high efficiency and ability to deliver a continuous flow of compressed air, making them a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
Overall, positive displacement compressors are a reliable and efficient choice for applications that require a steady supply of compressed air. Whether you need high pressure and low flow rates, or low noise levels and high efficiency, there is a positive displacement compressor that can meet your needs.
Dynamic Compressors
Dynamic compressors are a type of air compressor that works by imparting velocity to the air or gas and then converting that velocity into pressure. They are ideal for applications that require a lot of horsepower.
Centrifugal Compressors
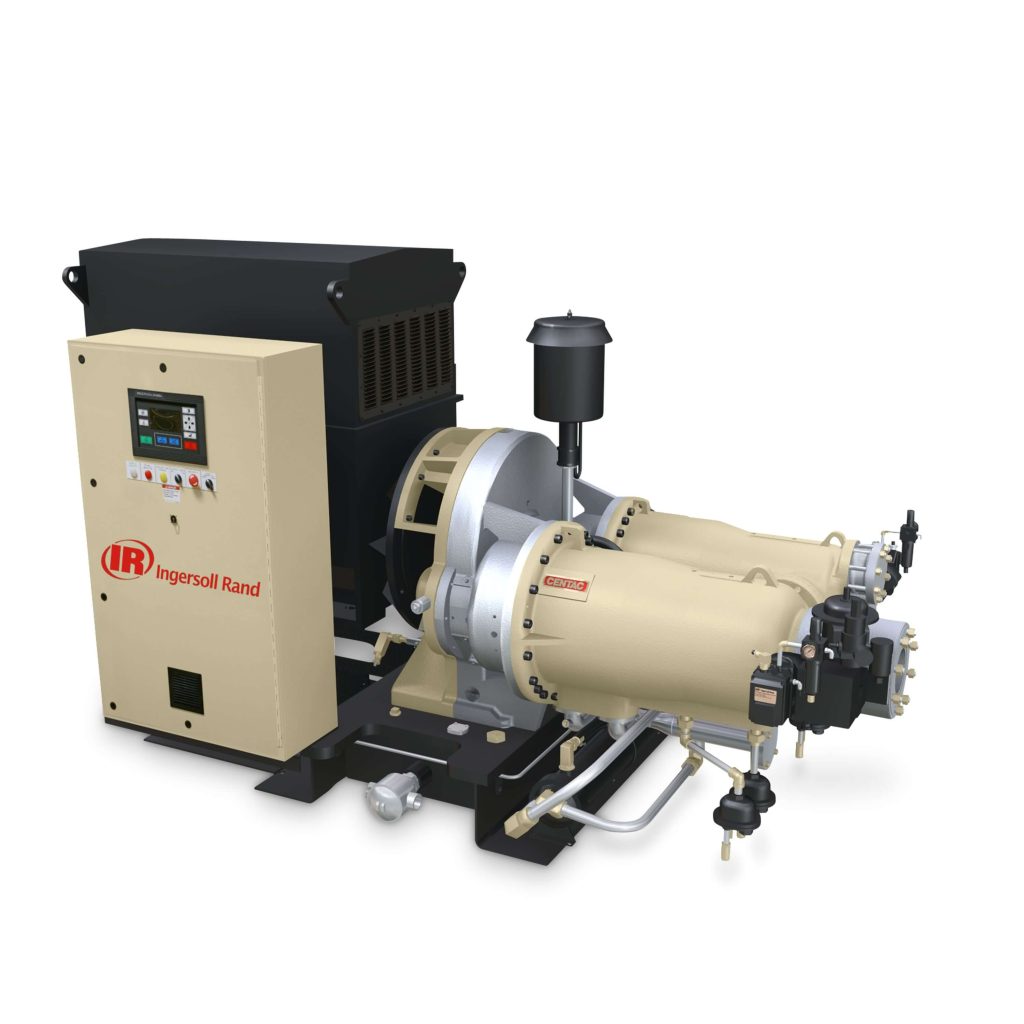

Centrifugal compressors are a type of dynamic compressor that use a rotating impeller to compress the air. The impeller accelerates the air radially outward and converts the velocity head into pressure. The compressed air then flows through a diffuser, which converts some of the velocity back into pressure. Centrifugal compressors are commonly used in large industrial applications, such as in power plants and petrochemical plants.
Axial Compressors

Photo courtesy of: Greg Goebel
Axial compressors are another type of dynamic compressor that use a series of rotating blades to compress the air. The blades are arranged in a series of stages, with each stage compressing the air further. The compressed air then flows through a diffuser, which converts some of the velocity back into pressure. Axial compressors are commonly used in aircraft engines and gas turbines.
Dynamic compressors are often used in applications that require high flow rates and high pressures, such as in gas pipelines and chemical processing plants. They are also used in applications that require a high degree of reliability, as they have fewer moving parts than positive displacement compressors. However, they are less efficient at low flow rates than positive displacement compressors.
Summing it all up, dynamic compressors are a type of air compressor that use velocity to compress air or gas. Centrifugal compressors and axial compressors are two types of dynamic compressors that are commonly used in industrial and aerospace applications.
Key Components of Air Compressors
When it comes to air compressors, there are several key components that work together to compress and store air. Understanding these components can help you choose the right type of air compressor for your needs.
Rotor or Piston Compressor
One of the most important components of an air compressor is the rotor or piston compressor. Reciprocating air compressors use pistons to compress the contents of an air cylinder and force them into a storage tank. On the other hand, rotary screw air compressors use twin screws or rotors instead of pistons to compress air.
Impeller or Lobe
Centrifugal air compressors use an impeller or lobe to compress air. The impeller is a rotating disk with curved blades that accelerates air to high speeds. The lobe is a rotating element with lobes that trap and compress air.
Shaft
The shaft is a rotating element that connects the motor to the compressor element. In centrifugal compressors, the shaft is connected to the impeller or lobe.
Filters
Filters are used to remove impurities from the air before it is compressed. Air compressors typically have two types of filters: intake filters and oil filters. Intake filters remove dust and debris from the air, while oil filters remove oil and other contaminants from the compressed air.
Cylinder
The cylinder is a part of the air compressor that houses the piston. In reciprocating air compressors, the cylinder is where the piston moves up and down to compress air. In some cases, air compressors may have multiple cylinders to increase the amount of compressed air.
Overall, understanding the key components of an air compressor can help you choose the right type of compressor for your needs. Whether you need a reciprocating, rotary screw, or centrifugal air compressor, knowing how each component works together can help you make an informed decision.
How Do I Choose the Right Type of Air Compressor?
When choosing an air compressor, there are several factors to consider to ensure that you get the right machine for your needs. Here are some of the most important factors to keep in mind:
Capacity
The capacity of an air compressor is one of the most important factors to consider. You need to make sure that the compressor you choose has enough capacity to power all of the tools you plan to use. The capacity of an air compressor is measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). You should choose a compressor with a CFM rating that is higher than the highest CFM rating of the tool you plan to use.
Efficiency
Efficiency is another important factor to consider when choosing an air compressor. A more efficient compressor will use less energy and save you money in the long run. Look for compressors that have high efficiency ratings and that are designed to operate at lower temperatures.
Cost
Cost is always a consideration when making any purchase, and air compressors are no exception. You should choose a compressor that fits within your budget, but you should also consider the long-term costs of operating the compressor. A more expensive compressor may be more efficient and have lower maintenance costs, which could save you money over time.
Maintenance
Maintenance is an important consideration when choosing an air compressor. You should look for compressors that are easy to maintain and that require minimal upkeep. Regular maintenance is important to keep your compressor running smoothly and to prevent costly breakdowns.
Noise
If you plan to use your compressor in a residential area or in a place where noise is a concern, you should choose a compressor that operates quietly. Look for compressors that have noise reduction features and that are designed to operate at lower decibel levels.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is another important factor to consider when choosing an air compressor. Look for compressors that are designed to operate at lower temperatures and that have high efficiency ratings. These compressors will use less energy and save you money on your energy bills.
Choosing an air compressor can be a daunting task, but by considering these factors, you can ensure that you get the right machine for your needs. Just remember to choose a compressor with enough capacity, high efficiency, low maintenance, low noise, and good energy efficiency.
Applications of Air Compressors
Air compressors are versatile machines that can be used for a wide range of applications. Here are some of the common uses of air compressors:
Tools
Air compressors are often used to power tools such as impact wrenches, nail guns, and sanders. These tools require a steady supply of compressed air to operate, and an air compressor can provide that supply.
Construction
Air compressors are commonly used in construction for tasks such as drilling, jackhammering, and concrete spraying. They can also be used to power pneumatic lifts and hoists.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, air compressors are used for a variety of tasks such as powering pneumatic tools, operating conveyor systems, and controlling robotic equipment. They can also be used for air blow-off and vacuum applications.
Cleaning
Air compressors can be used for cleaning tasks such as blowing dust and debris off of machinery and work surfaces. They can also be used for cleaning carpets and upholstery.
Painting
Air compressors are commonly used in painting applications to power paint spray guns. They provide a steady stream of compressed air that atomizes the paint and allows it to be sprayed onto surfaces.
Construction Sites
Air compressors are often used on construction sites to power a variety of tools and equipment. They can also be used to provide compressed air for cleaning and painting tasks.
Overall, air compressors are an essential tool for a wide range of applications. Whether you are working in construction, manufacturing, or just need to power some tools, an air compressor can provide the compressed air you need to get the job done.
Air Compressor Power Sources
When it comes to air compressors, the power source is an essential factor to consider. The most common power sources for air compressors are electric motors and natural gas.
Electric Motor
Electric motors are the most popular power source for air compressors. They are reliable, efficient, and easy to use. Electric motors come in different horsepower (HP) ratings, which determine the amount of power the motor can produce. The higher the horsepower, the more air pressure the compressor can generate.
Power
The power of an air compressor is measured in horsepower (HP). The higher the horsepower, the more air pressure the compressor can generate. Most compressors have a limit on the PSI they can produce. For example, single-stage compressors can only reach 125 PSI. A higher PSI generally allows you to use the air compressor for extended periods.
Natural Gas
Natural gas is another power source for air compressors. It is more cost-effective than electricity, and it produces fewer emissions. However, natural gas compressors are less common than electric compressors.
When choosing a power source for your air compressor, consider the availability of the power source, the cost of the power source, and the amount of power you need. If you need a portable compressor, electric compressors are a better choice. If you need a stationary compressor, natural gas may be a more cost-effective option.
Overall, the power source of your air compressor is an essential factor to consider. Choose the power source that best suits your needs and budget.
Understanding the Efficiency of Air Compressors
When it comes to air compressors, efficiency is a crucial factor to consider. Not only does it affect the running costs of the compressor, but it also impacts the overall performance and lifespan of the machine. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at the efficiency of air compressors and how it affects various aspects of the machine.
Heat and Energy Consumption
One of the main factors that affect the efficiency of an air compressor is the amount of heat generated during operation. As the compressor compresses air, it generates heat, which can cause the machine to overheat and reduce its efficiency. To combat this, many air compressors are equipped with cooling systems that help dissipate the heat and keep the machine running smoothly.
Another factor that affects efficiency is energy consumption. The more energy an air compressor uses, the less efficient it is. This is why it’s important to choose an air compressor that is designed to be energy-efficient, as it can help reduce your energy bills and lower your overall running costs.
Pressure Increase and Running Costs
The pressure increase that an air compressor can achieve is another important factor to consider when evaluating its efficiency. The higher the pressure increases, the more efficient the compressor is at compressing air. However, it’s important to note that higher pressure increases often come with higher running costs, as the machine needs to work harder to achieve these higher pressures.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a critical factor to consider when choosing an air compressor. An energy-efficient compressor can help reduce your energy bills and lower your overall running costs. One way to evaluate the energy efficiency of an air compressor is to look at its Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER). The EER is a measure of the amount of cooling output per unit of energy input, and a higher EER means that the machine is more energy-efficient.
In conclusion, understanding the efficiency of air compressors is crucial when choosing the right machine for your needs. By considering factors such as heat generation, energy consumption, pressure increase, running costs, and energy efficiency, you can make an informed decision and choose an air compressor that will provide reliable performance while keeping your costs under control.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 3 basic types of compressors?
There are three basic types of compressors: positive displacement compressors, dynamic compressors, and hybrid compressors. Positive displacement compressors trap air and then compress it by reducing the volume of the air chamber. Dynamic compressors use high-speed rotating impellers to accelerate air and then slow it down, which increases its pressure. Hybrid compressors combine the features of both positive displacement and dynamic compressors.
What are the different types of air compressors?
There are several different types of air compressors, including reciprocating compressors, rotary screw compressors, centrifugal compressors, axial compressors, and scroll compressors. Each type of compressor has its own unique set of advantages and disadvantages, which make them suitable for different applications.
What are the 4 most common air compressors?
The four most common air compressors are reciprocating compressors, rotary screw compressors, centrifugal compressors, and axial compressors. Reciprocating compressors are the most common type of compressor and are used in a wide range of applications, including automotive repair, construction, and manufacturing. Rotary screw compressors are also very common and are often used in industrial settings. Centrifugal compressors are typically used in large-scale industrial applications, such as power generation and natural gas processing. Axial compressors are used in applications where high flow rates are required.
What are the three most common air compressors?
The three most common air compressors are reciprocating compressors, rotary screw compressors, and centrifugal compressors. Reciprocating compressors are the most common type of compressor and are used in a wide range of applications, including automotive repair, construction, and manufacturing. Rotary screw compressors are also very common and are often used in industrial settings. Centrifugal compressors are typically used in large-scale industrial applications, such as power generation and natural gas processing.
What are the working principles of rotary screw compressors?
Rotary screw compressors operate on the principle of positive displacement. Filtered air enters the inlet of the airend where male and female rotors un-mesh. The air is trapped between the rotors and the airend housing. The air is then compressed as the rotors rotate and the volume of the air chamber is reduced. The compressed air is then discharged through the outlet.
How are reciprocating air compressors used in construction?
Reciprocating air compressors are commonly used in construction for a variety of tasks, including powering pneumatic tools, such as jackhammers, nail guns, and sanders. They are also used to power air-operated pumps and to supply air for sandblasting. Reciprocating compressors are popular in construction because they are relatively inexpensive, durable, and easy to maintain.
Feature image: Photo by Jared Schwitzke on Unsplash


